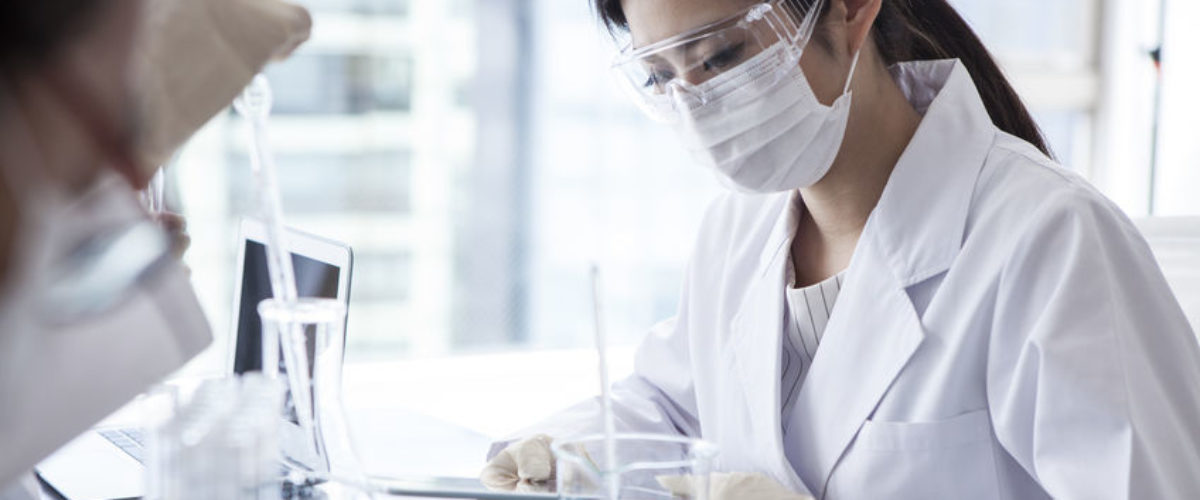
The Breath Hydrogen Test " BHT "is a test that assesses the intestinal digestion of lactose (milk sugar) and to detect a lactose intoleranceThis syndrome is defined by the inability of the intestinal cells to break down the lactose in simple sugars (glucose and galactose) due to a lactase enzyme deficiency.
Lactose intolerance is defined as the inability of the body to assimilate milk sugar. This intolerance occurs when the body does not produce enough lactase : lactose ferments in the digestive tract, causing symptoms of varying severity depending on the degree of intolerance.
The symptoms of lactose intolerance can be confused with other conditions, which is why it's important to pinpoint the cause of these digestive problems. There are several types of test that can be used to confirm or rule out lactose intolerance. Breath Test is one of them.
What is the Breath Test?
The Breath Test or Breath Hydrogen Test (BHT) assesses the intestinal digestion of lactose in order to detect possible lactose intolerance.
When we are lactose intolerant, the intestinal cells are unable to break down lactose into the simple sugars galactose and glucose. This is due to a lack of the enzyme lactase in the body.
The Breath Test is the most commonly performed test to remove any uncertainty about lactose intolerance. The Breath Test is performed in medical settings, usually in hospital gastroenterology departments, to diagnose a problem with sugar digestion, and detects the presence and amount of exhaled hydrogen.
In concrete terms, a Breath Test lasts 3 to 4 hours: the patient must absorb 10 to 50g of lactose (or 200 to 300 ml of cow's milk) and then exhale into a mouthpiece every 30 minutes in order to measure the quantity of hydrogen exhaled. If the patient has difficulty digesting lactose, digestion is incomplete and hydrogen is released into the intestine through fermentation by intestinal bacteria. The hydrogen produced passes through the bloodstream to the lungs, so the more hydrogen in the exhaled air, the less able the patient is to tolerate lactose.
A Breath Test should be performed on an empty stomach. For the test to be reliable, a number of foods that could lead to fermentation should be avoided: milk, cabbage, starchy foods and fruit juices. It is also important to avoid taking antibiotics two to four weeks before the test.
What is the purpose of the Breath Test?
The Breath Test is a reliable and accurate test for intolerance and is safe, but it can be unpleasant due to the lactose absorbed.
The Breath Test may be prescribed by your doctor in case of chronic symptoms such as bloating, diarrhoea, abdominal pain or vomiting, and if there is a suspicion of lactose intolerance.
If the Breath Test reveals lactose intolerance, the patient can adjust his or her diet accordingly and/or plan lactase enzyme supplementation. This supplementation will take the form of lactic acid bacteria capsules or lactase capsules.
The Lactolerance range offers three types of food supplements: Lactolerance One Day, taken daily for permanent protection 24 hours a day, and Lactolerance 4500 and 9000 for moderate or severe intolerance, taken on demand. These food supplements suppress the symptoms of lactose intolerance and therefore offer the possibility of consuming lactose freely.
How does the BHT work?
This is the test the most commonly used test for the definitive diagnosis of lactose intoleranceIt lasts from 3 to 4 hoursIt is reliable and very specific and does not have no risk. Several conditions must be met before the test is carried out: it is recommended not to use antibiotics two to four weeks before the test and laxatives three days before the test. The day before the test, no milk, fruit juices or foods that cause hyperproduction of intestinal gas such as starchy foods and cabbage should be consumed. The patient must fast for at least 6 hours before the test, but can drink water at any time.
After absorbing 10 to 50 g of lactose or 200-350 ml cow's milkthe person exhales into a mouthpiece every 30 minutes to measure the amount of hydrogen exhaled.
What is the purpose of this test?
The principle of the test is simple, the lactose poorly digested at the intestinal level undergoes fermentation by colonic bacteria with hyperproduction of hydrogen which will pass through the bloodstream to the lungs. The patient at rest does not produce hydrogen, so any increase in the level of hydrogen exhaled is necessarily due to this fermentation.. The more hydrogen there is in the breath, the greater the lactase deficiency. In very rare cases, the bacteria in the colon do not produce hydrogen even in cases of lactose intolerance.
The doctor may prescribe a exhaled hydrogen test in case of various digestive symptoms, such as bloating, abdominal pain, transit disorders (diarrhoea, vomiting) or also in case of suspected intolerance to other sugars such as glucose or fructose (fruit sugar).
It should be noted that if lactose intolerance is suspected, the first step is to carry out a complete exclusion of foods containing lactose for 3 days to see if the symptoms improve or not, it is the eviction test. The eviction test becomes unnecessary in cases of irritable bowel syndrome or known bowel disease.

Hello, I'm Vincent
Like you, I'm lactose intolerantI know exactly what you're going through and the difficulties you encounter on a daily basis. For over 10 years, I've been helping our customers to use our dietary supplements and giving advice and tips on how to improve their digestive comfort. I'm also a keen cook and gourmet, so you'll find my favourite recipes for a lactose-free diet in this blog.
Lactose intolerance is not inevitable! With LACTOLERANCE you can digest with complete peace of mind